Our latest EV Charging webinar explored the most up-to-date trends, insights and predictions about the adoption of EV charging infrastructure. If you’ve missed that or want to re-watch it, we’ve gathered all the best moments from the webinar for you. Excited? Read on!
We at OKdo are passionate about tech and always aim to be the first to learn all the latest trends in the industry. So, we were thrilled to have Naeem Farooqi, CEO & Founder at Fleet Zero, Marc Palmer, Brand Director at Auto Trader UK, and Richard Curtin, Co-Founder & CTO at OKdo, speak about the possibilities of innovating EV charging with our smart technologies.
If you’re excited to discover the hottest insights & trends on EV charging infrastructure and the role of single-board computers, as well as to learn how we can help scale up your charging business with our best-in-class hardware and software solutions, read on!
Meet the Speakers

RICHARD CURTIN
Co-founder & CTO at OKdo
Richard will share how you can adopt smart EV charging solutions and get ahead of the game with OKdo.
What’s the future of EVs in the UK? Top 5 EV charging trends
Marc Palmer, Brand Director at Auto Trader UK has shared his vision and predictions regarding the development of EV charging infrastructure in the UK in 2023 and the years to come.
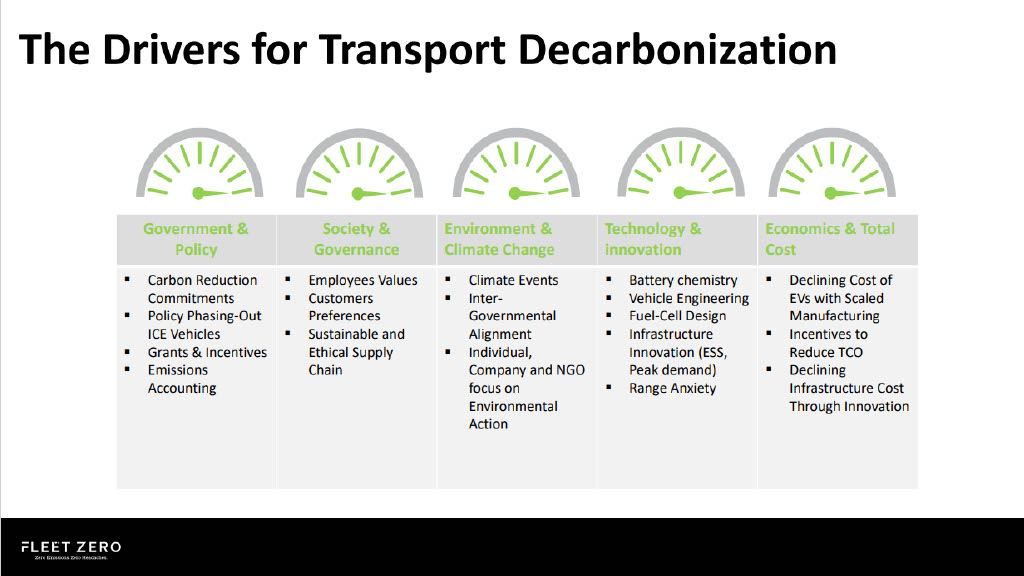
According to Marc, 2023 is a pivotal year, a year when we begin a “once-in-an-industry change” to support the adoption of EVs. Curious to learn more? Discover some of the top trends & predictions below.
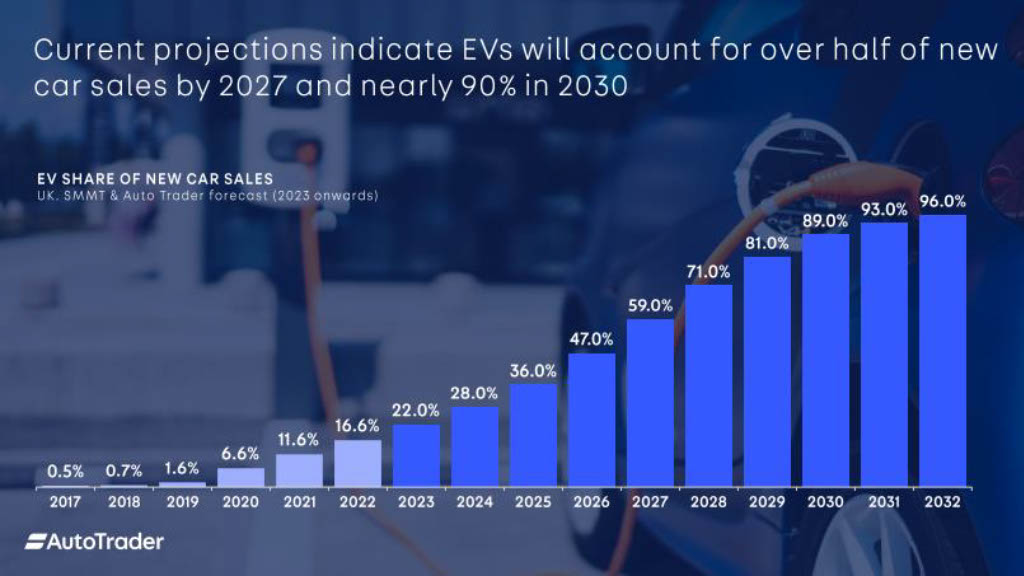
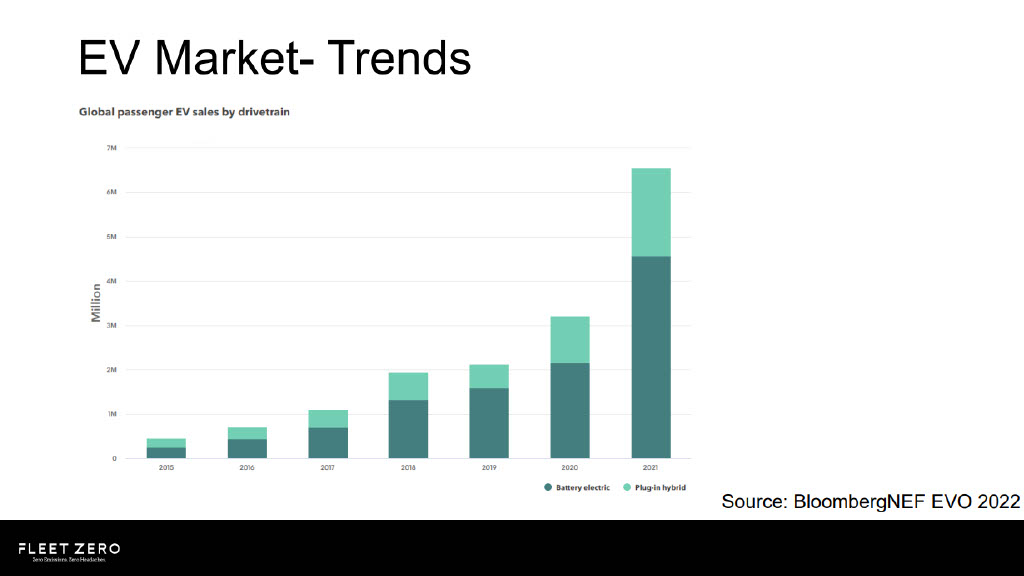
EVs share of new car sales will continue to grow
It is predicted that electric vehicles will make up over half of the new car sales by 2027 and nearly 90% in 2030.
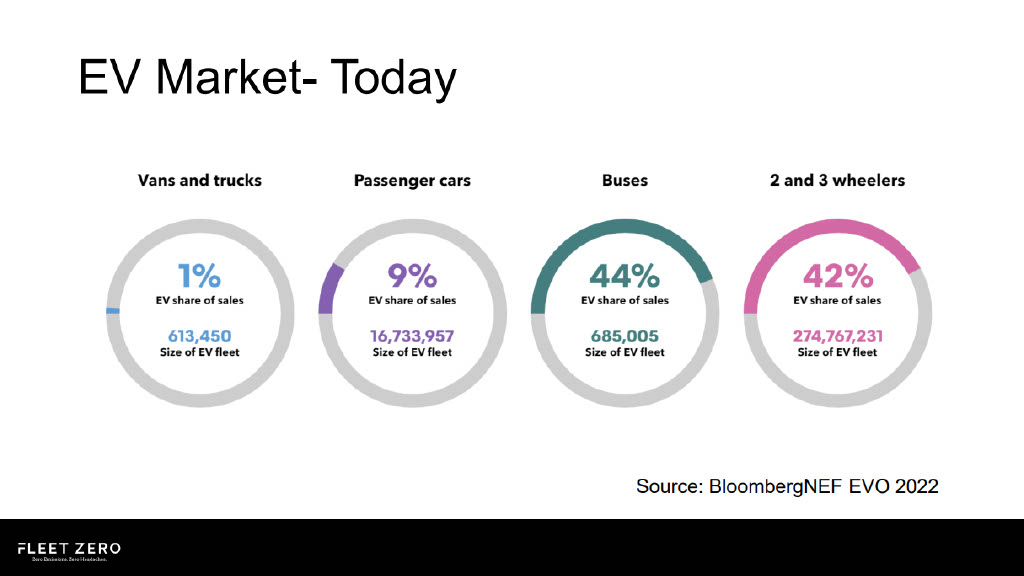
In the UK, nearly a quarter of cars on the road will be electric by 2030. Whereas, in 2023, only 3% of cars on British roads are electric.

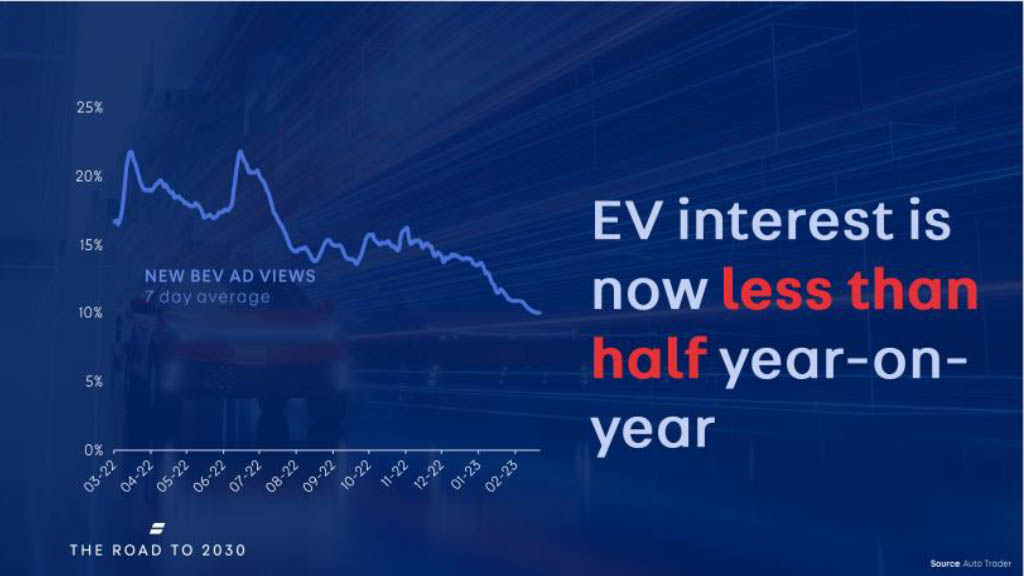
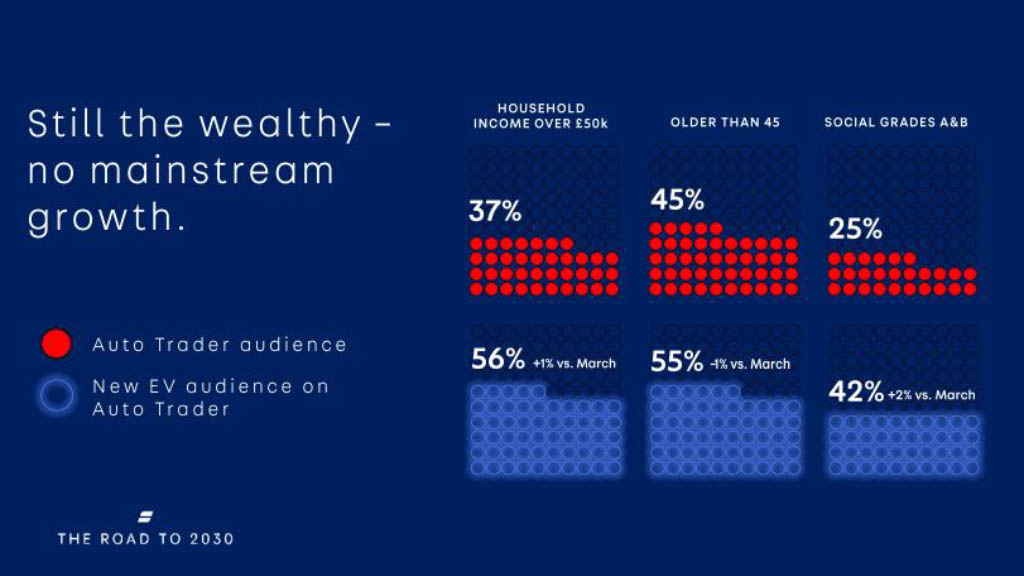
EV Interest is on the rise
According to data provided by Autotrader UK, consumers are becoming more and more interested in electric vehicles and are considering this option when searching for a new car purchase.
Some of the key stats:
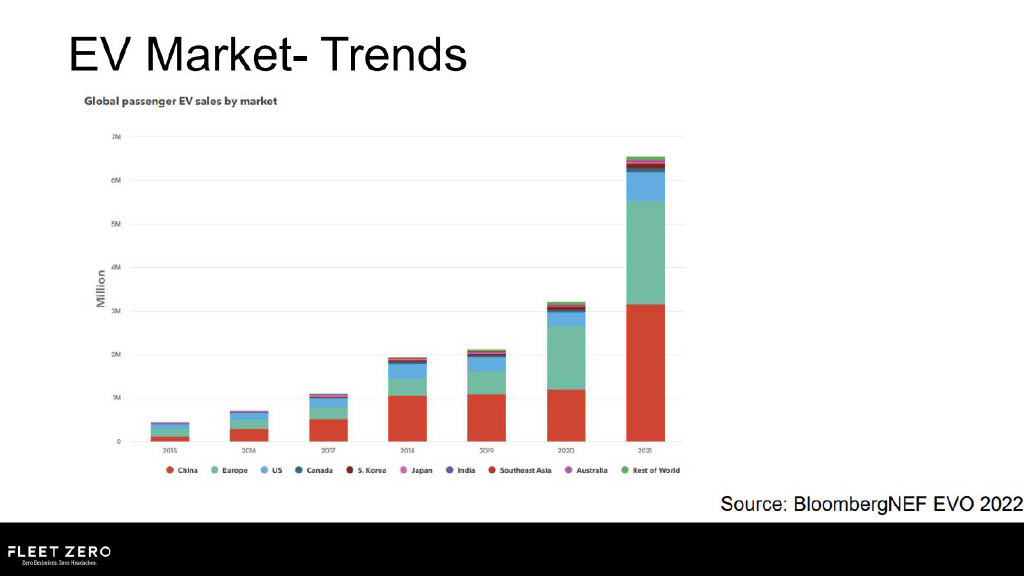
- 1 in 4 of all new car views in 2022 are EVs, which is 4 times higher than in 2020;
- There is a 77% increase in public charge points vs 2020;
- Consumers now have over 70 different models of EVs to choose from.
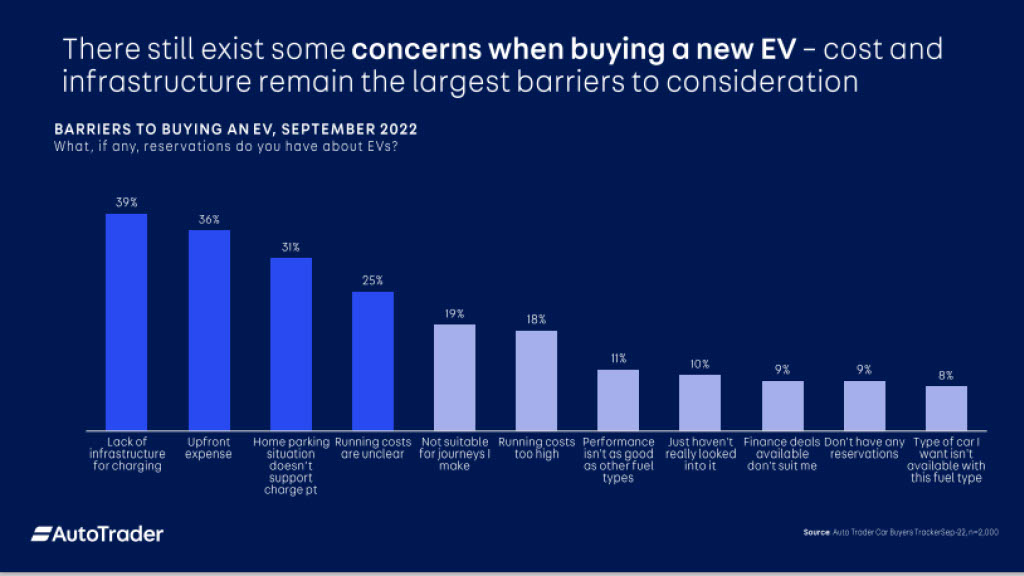
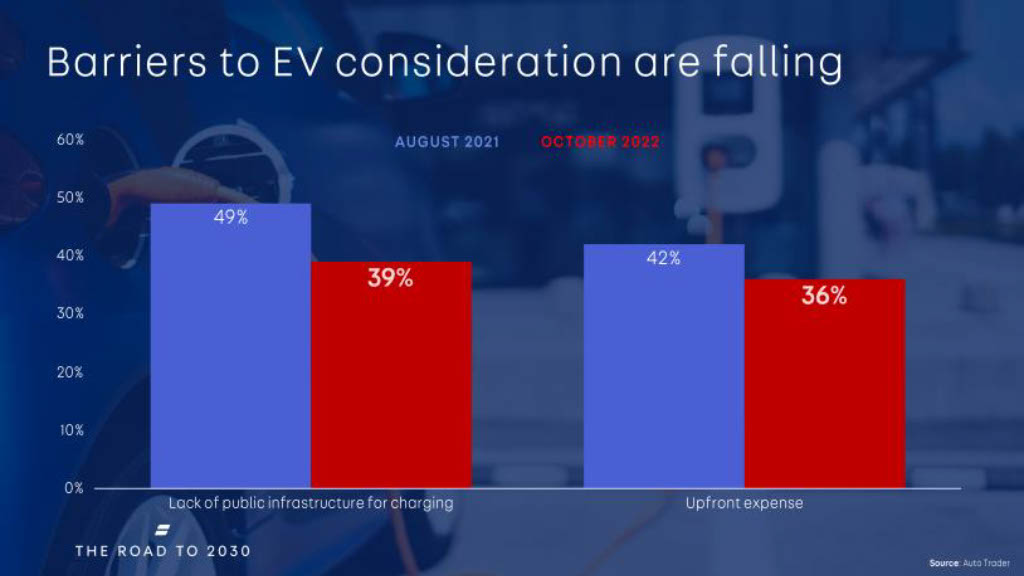
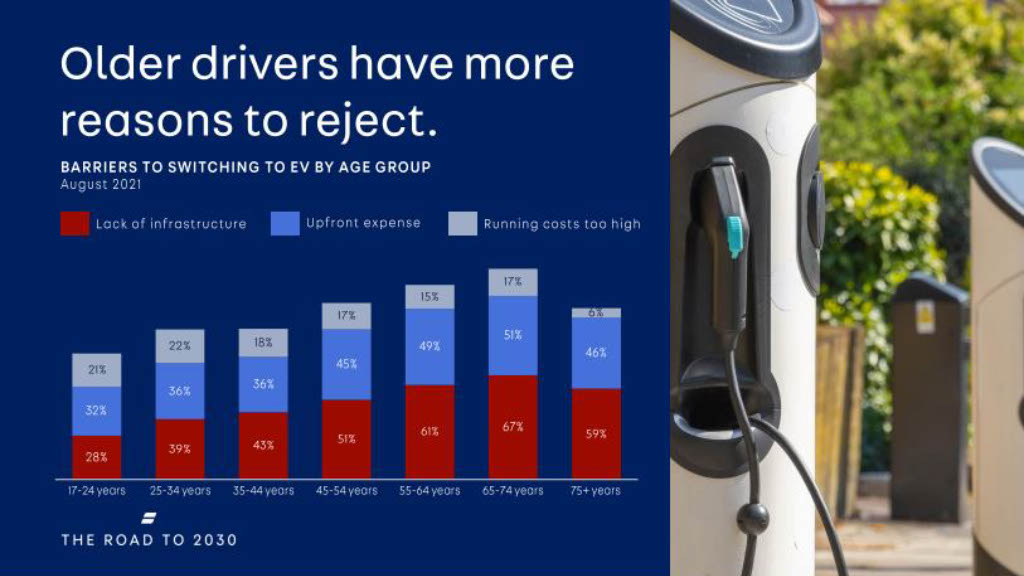
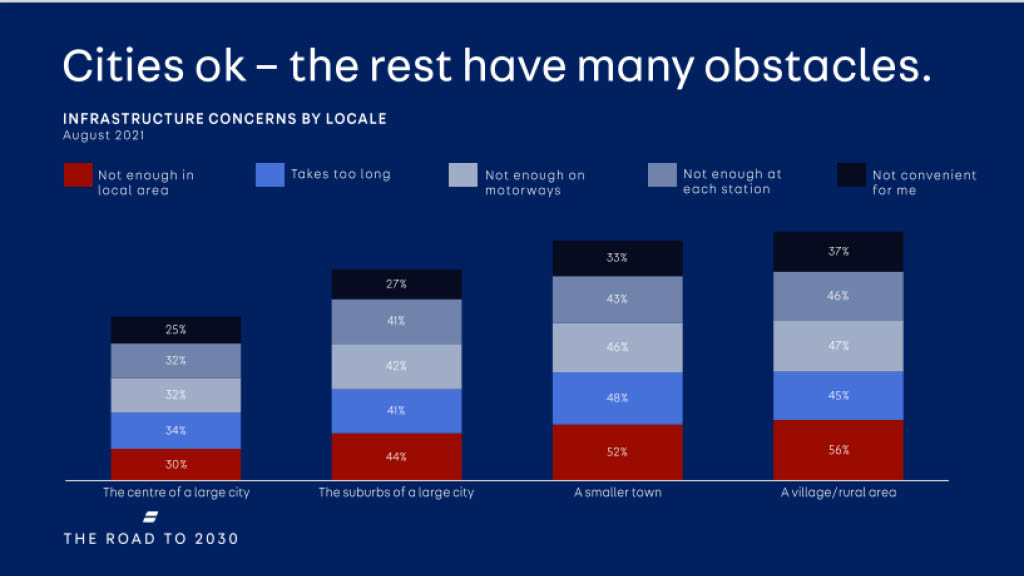
Barriers to EV adoption
The main barriers that consumers face when purchasing a new electric vehicle are cost and infrastructure.
The largest reservation has been found to be a lack of public infrastructure for charging across the country, especially in smaller towns and rural areas.
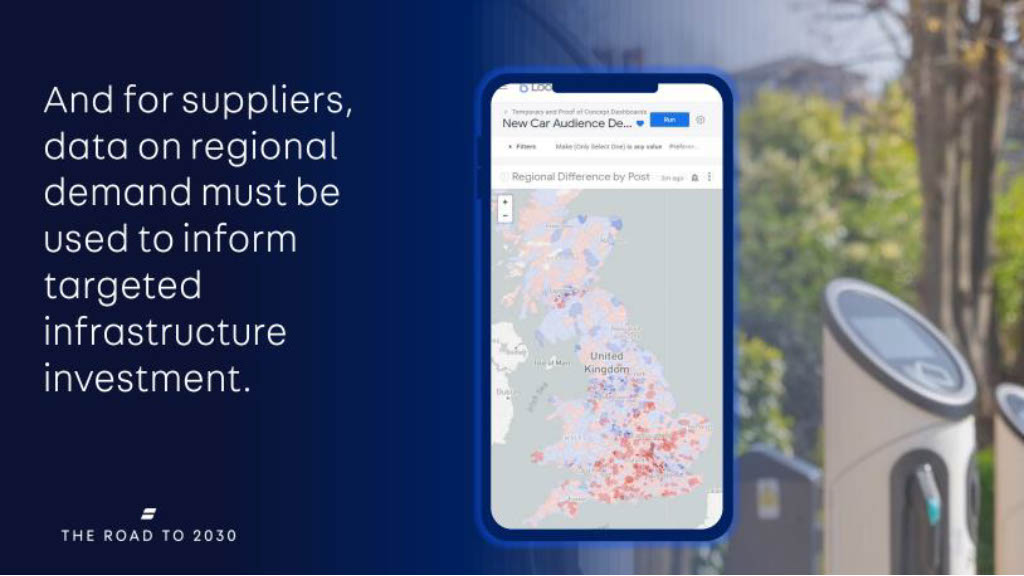
As the UK government has banned the sale of new petrol and diesel cars by 2030, developing an accessible EV charging infrastructure across the country, in all regions, should become the #1 priority as soon as 2023.
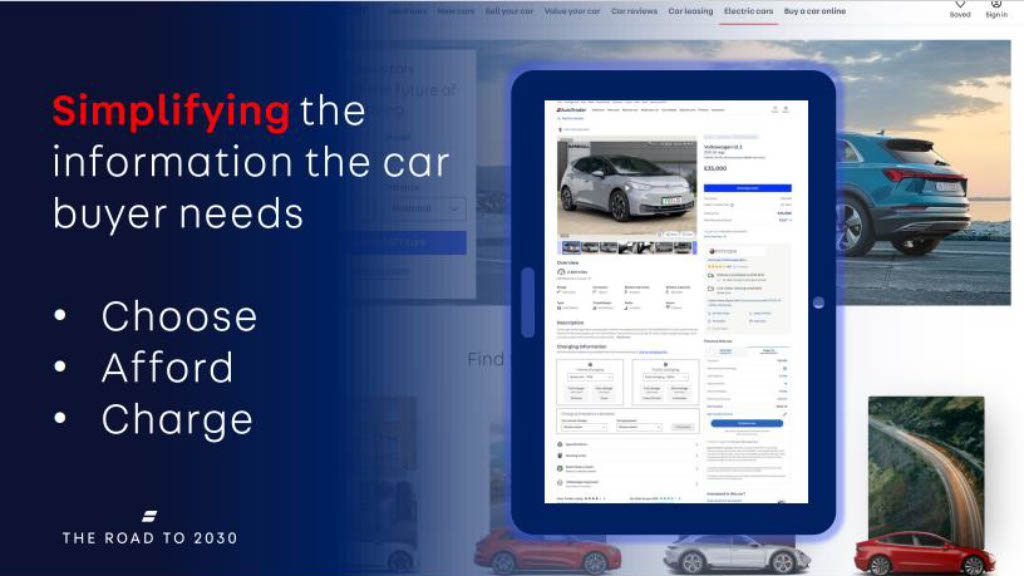
Simplicity is key
It is time to re-energise! To boost the adoption of EVs, simplicity is key. Simplifying the information about the car will make a significant impact. The top 3 things a buyer considers when evaluating options are:
- Basic information – Details on charging, the distance it can drive on a full charge, etc.
- Affordability – the price point of EVs is an issue for both younger and older consumers. At the moment, there is a 39% premium on electric vehicles.
- Charging – are there enough available public charging points? Even if, at the moment, 80% of owners charge their electric cars at home, having access to public EV charging infrastructure is still a key criteria that consumers consider.

SBCs for EV
SBCs are the perfect cost-effective solution for EV charging station development, being an application that requires more processing power than microcontrollers can provide.
SBCs such as ROCK are convenient, secure, powerful and reliable, and what’s more – extremely versatile, capable of boosting your development to a new level. Learn more about how SBCs can help when building EV charging stations below.
SBCs as your ultimate helper in EV charging station development
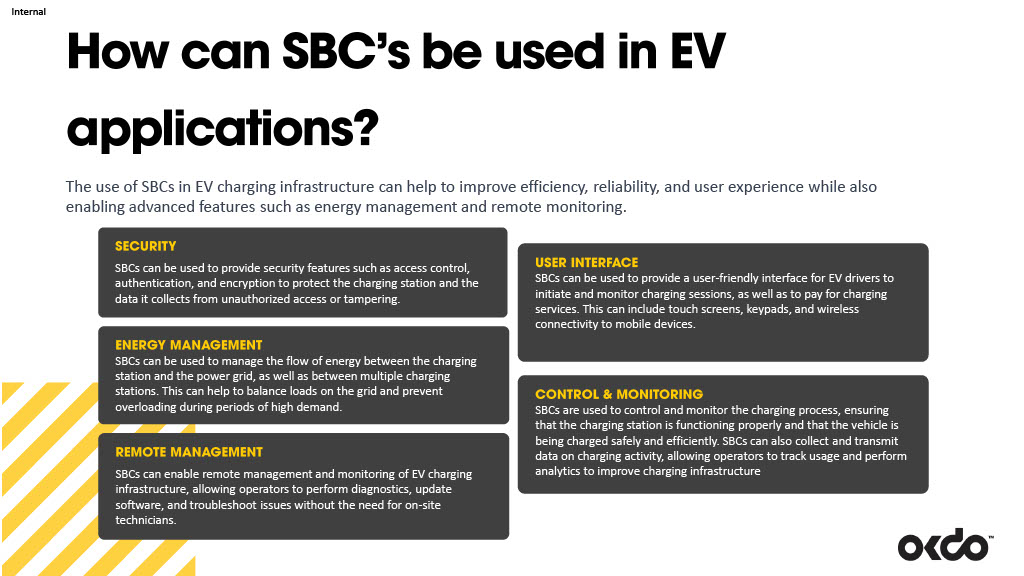
Looking for ways to build your own EV charging station? Single Board Computers (SBCs) come to the rescue! The use of SBCs in EV charging infrastructure can help to improve efficiency, reliability, and user experience while also enabling advanced features such as energy management and remote monitoring.
How can SBCs be used in EV Applications?
- Security: SBCs can be used to provide security features such as access control, authentication, and encryption to protect the charging station and the data it collects from unauthorized access or tampering.
- Energy management: SBCs can be used to manage the flow of energy between the charging station and the power grid, as well as between multiple charging stations. This can help to balance loads on the grid and prevent overloading during periods of high demand.
- Remote management: SBCs can enable remote management and monitoring of EV charging infrastructure, allowing operators to perform diagnostics, update software, and troubleshoot issues without the need for on-site technicians.
- User interface: SBCs can be used to provide a user-friendly interface for EV drivers to initiate and monitor charging sessions, as well as to pay for charging services. This can include touch screens, keypads, and wireless connectivity to mobile devices.
- Control & monitoring: SBCs are used to control and monitor the charging process, ensuring that the charging station is functioning properly and that the vehicle is being charged safely and efficiently. SBCs can also collect and transmit data on charging activity, allowing operators to track usage and perform analytics to improve charging infrastructure.



Why SBCs are your perfect choice for EVs?
POWER
- SBCs have reduced power requirements due to their minimalist design.
- SBCs are cost-effective and suitable for applications that require more processing power than microcontrollers can provide.
RELIABILITY
- SBCs have a proven track record of reliable performance in industrial environments.
- They have fewer maintenance issues and longer lifespans compared to desktop computers.
- SBCs are designed to withstand vibration, shock, and extreme temperatures, making them suitable for automotive, aerospace, and military domains.
SECURITY
- Secure Boot is a feature that ensures the system only runs trusted code during boot-up.
- It prevents unauthorized software from running on the system, reducing the risk of malware infections and other security threats.
- The TPM chip stores the private keys used to sign trusted boot code, ensuring that only authorized code can be loaded.
SPACE
- SBCs are ultra-compact due to their minimalist design.
- They can be easily integrated into existing equipment and reduce overall system size.
- ROCK SBCs can be customised to reduce waste and cost.
CONVENIENCE
- Troubleshooting and upgrading is easier with only one circuit board to deal with.
- OKdo can offer support from talented engineers that can help develop a custom solution for your needs.
Missed the webinar? Watch the recording on-demand

Haven’t had the chance to watch our webinar live, or didn’t know we were running one? We’ve got you covered. Watch the webinar recording to catch up with all our incredible finds around EV Charging.
Webinar Slide Deck
Curious to take a closer look at the insights & trends presented at the webinar? Here’s the webinar slide deck:
Webinar Q&A. Here’s all you wanted to know about EV Charging Infrastructure
Q&A:
Question. How likely is it that cobalt will run out?
Answer. It is difficult to predict with certainty when or if cobalt will run out. Cobalt is a finite resource, and its supply is dependent on a variety of factors, including global demand, mining practices, and exploration efforts.
Current estimates suggest that there are significant reserves of cobalt globally, particularly in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which accounts for over half of global production. However, there are concerns about the environmental and social impacts of cobalt mining in the DRC, as well as the potential for supply chain disruptions due to political instability in the region.
Additionally, as demand for electric vehicles and other high-tech products that use cobalt continues to increase, there may be pressure on global supplies. However, there are efforts underway to reduce the amount of cobalt required in these products and to develop alternative materials. While it is possible that cobalt could become scarce in the future, there are currently significant reserves and ongoing efforts to mitigate supply chain risks and reduce demand for cobalt.

Question. The projected increase in EV-related fires really surprised me. If this is due to cables being run over, is there scope for battery management systems to detect electricity arriving through these damaged cables and shut down? Are these fires preventable?
Answer. Electric vehicle (EV) fires are a concern, as with any type of vehicle. However, it’s worth noting that EVs are no more prone to fires than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. The risk of fire can be reduced through proper design, manufacturing, and maintenance of the vehicle and its components.
In the case of EV fires caused by damaged charging cables, there are several ways to prevent them. One approach is to use charging stations with automated cable management systems that can retract the cable when it’s not in use, reducing the risk of damage. Additionally, EV manufacturers can design their battery management systems to detect anomalies in the charging process, such as unexpected voltage surges or drops, which could indicate a damaged cable. The battery management system can then shut down the charging process to prevent an overheating and potential fire.
There are also safety standards and regulations in place that EV manufacturers must adhere to, including requirements for battery safety, charging system safety, and crash safety. These regulations help ensure that EVs are safe and reliable for consumers. While EV fires can occur, there are measures in place to prevent them and ongoing efforts to improve the safety and reliability of EVs.

Question: What are some of the biggest challenges facing the electric vehicle industry today, and how can we work to address them?
Answer. The electric vehicle (EV) industry is rapidly growing and evolving, but there are still several challenges facing the industry that need to be addressed in order to accelerate the adoption of EVs. Some of the biggest challenges include:
- Range anxiety: Many consumers are still concerned about the range of EVs and the availability of charging infrastructure. To address this challenge, governments and the private sector need to invest in building out charging infrastructure, particularly in urban areas and along major transportation corridors.
- Battery technology and cost: Battery technology is a critical component of EVs, and improving battery technology is essential to increasing the range and reducing the cost of EVs. Continued research and development, as well as investments in battery manufacturing, will be important to improving battery technology and reducing the cost of EVs.
- Supply chain challenges: The supply chain for EVs is complex and involves many different components, including batteries, electric motors, and other specialised components. There is a need for a secure, reliable, and sustainable supply chain for these components, particularly for critical minerals like lithium and cobalt.
- Consumer education and awareness: Many consumers are still unfamiliar with EVs and how they work, which can make it difficult to convince them to switch from traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. More education and awareness campaigns are needed to help consumers understand the benefits of EVs and how they can be integrated into their daily lives.
- Policy and regulatory support: Government policies and regulations play a critical role in shaping the EV industry. Policies that support EV adoption, such as tax incentives and subsidies, can help to accelerate the transition to electric transportation.
Addressing these challenges will require a collaborative effort from industry stakeholders, governments, and consumers. Continued innovation like at OKdo, investment, and education will be essential to accelerating the adoption of EVs and reducing the environmental impact of transportation.

Question. Is there any possibility to produce a vehicle without a battery? Or is there any possibility to produce a battery without the minerals? Because cobalt and lithium, all these are minerals under the soil. So it’s again depleting the environment like fossil fuel.
Answer. At this time, it is not possible to produce an electric vehicle (EV) without a battery. Batteries are essential to store and provide the electrical energy required to power an EV. However, there are ongoing efforts to develop alternative energy storage technologies that could be used in place of traditional batteries, such as hydrogen fuel cells or capacitors.
Regarding the minerals required to produce batteries, it is true that some of these minerals, such as cobalt and lithium, are finite resources that are extracted from the earth. However, there are efforts underway to reduce the amount of these minerals required in battery production, to develop alternative materials that can be used in batteries, and to recycle and reuse batteries to reduce the need for new mining.
For example, some manufacturers are developing batteries that use alternative materials, such as sodium or zinc, that are more abundant and widely available than some of the minerals currently used in batteries. Additionally, there are efforts to improve battery recycling processes to recover valuable materials from used batteries and reduce the environmental impact of battery production.
While it is not currently possible to produce an EV without a battery, ongoing research and development in battery technology and alternative energy storage technologies may lead to new solutions in the future that are more sustainable and environmentally friendly.

Question. Why are solar-powered EVs not being taken into account as a potential solution to the significant challenges faced by the EV charging network?
Answer. Solar-powered EVs are an interesting concept, but they are not yet a practical solution for addressing the challenges faced by the EV charging network. There are several reasons for this:
- Solar panels on EVs are not yet efficient enough to provide a significant amount of energy: While solar panels have become more efficient in recent years, they are still not efficient enough to provide a significant amount of energy to power an EV. In most cases, solar panels on an EV would only be able to provide a small amount of energy to supplement the battery.
- Limited space on EVs: EVs have limited space for installing solar panels, and the size and weight of the solar panels can affect the performance of the vehicle. Installing large solar panels on an EV would also increase the cost of the vehicle and make it less practical for most consumers.
- Lack of charging infrastructure: Even if EVs were equipped with solar panels, there would still be a need for charging infrastructure to provide energy when the vehicle is not in use or when the solar panels are not generating enough energy. Building out a comprehensive charging network will still be necessary to support the widespread adoption of EVs.
While solar-powered EVs are not currently a practical solution for addressing the challenges faced by the EV charging network, solar energy can still play an important role in supporting EV charging infrastructure. Solar panels can be installed at charging stations to provide clean energy for charging EVs, reducing the carbon footprint of the charging process.

Question. How does the rate of the shift from ICE to EV compare to the late-80’s when we moved from leaded fuel to unleaded?
Answer. The rate of the shift from internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to electric vehicles (EVs) is difficult to compare directly to the shift from leaded fuel to unleaded fuel in the late 1980s, as there are many factors that influence the pace of adoption.
However, it is worth noting that the transition to EVs is happening faster than many experts had predicted. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number of EVs on the road, driven by factors such as falling battery prices, government incentives, and increasing consumer awareness of the environmental benefits of EVs. In some countries, such as Norway and Iceland, EVs now make up a significant percentage of new vehicle sales, and many major automakers have announced plans to phase out ICE vehicles in the coming years.
By comparison, the shift from leaded to unleaded fuel took several decades to complete, with the first regulations banning leaded fuel introduced in the 1970s and the final phase-out of leaded fuel not occurring until the early 2000s. The transition was driven by concerns about the health and environmental impacts of leaded fuel, as well as improvements in technology that made unleaded fuel a viable alternative.
While the pace of the shift to EVs is not directly comparable to the transition from leaded to unleaded fuel, the growth in the EV market is a positive sign for the future of sustainable transportation. With continued innovation and investment, it is possible that EVs could eventually replace ICE vehicles as the primary mode of transportation, reducing carbon emissions and improving air quality in cities around the world.

Question. What are some of the most promising innovations in the electric vehicle industry today, and how are they likely to impact the market in the near future?
Answer. There are several promising innovations in the electric vehicle (EV) industry that are likely to impact the market in the near future. Examples include:
- Solid-state batteries: Solid-state batteries are a new type of battery technology that use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte, which can offer advantages in terms of safety, energy density, and charging speed. Several companies, including Toyota and BMW, are working on developing solid-state batteries for use in EVs.
- Wireless charging: Wireless charging technology allows EVs to be charged without the need for physical cables or plugs. This technology could make charging more convenient for EV owners and help to reduce the demand for traditional charging infrastructure.
- Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology: V2G technology allows EVs to store energy and feed it back into the electrical grid when it is needed, which can help to balance supply and demand and improve the reliability of the grid. This technology could also provide a source of revenue for EV owners, who could sell the stored energy back to the grid.
- Fast charging: Fast charging technology allows EVs to be charged more quickly, reducing the amount of time that drivers need to spend charging their vehicles. Several companies, including Tesla and Porsche, are investing in fast charging technology to help make EVs more convenient for consumers.
- Lightweight materials: Lightweight materials, such as carbon fibre and aluminium, can help to reduce the weight of EVs and improve their range and performance. Several automakers, including BMW and Audi, are using lightweight materials in their EVs to help make them more competitive with traditional ICE vehicles.
These innovations are likely to have a significant impact on the EV market in the near future, helping to make EVs more convenient, efficient, and affordable for consumers. As these technologies continue to evolve and improve, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the EV industry in the years to come.

Question: Over the lifetime of the vehicle, is there any data for comparison on the carbon footprint of EV vs ICE?
Answer. Yes, there is data available that compares the carbon footprint of electric vehicles (EVs) versus internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles over their lifetime. Generally, studies have found that EVs have a lower carbon footprint compared to ICE vehicles, even when accounting for the emissions associated with the production of the batteries and the electricity used to charge the EVs.
One study by the Union of Concerned Scientists found that EVs in the United States have significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to the average new gasoline-powered vehicle, even when taking into account the emissions associated with battery production and electricity generation. The study found that EVs produced less than half the emissions of the average new gasoline-powered vehicle in the United States when charged with the average U.S. electricity mix.
Another study by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) found that EVs in Europe have lower lifetime greenhouse gas emissions than ICE vehicles, with emissions reductions ranging from 17% to 30% depending on the size of the vehicle and the country in which it is driven.
Overall, the carbon footprint of an EV versus an ICE vehicle will depend on a number of factors, including the source of the electricity used to charge the EV, the efficiency of the vehicle, and the emissions associated with the production and disposal of the vehicle and its components. However, in most cases, EVs are likely to have a lower carbon footprint compared to ICE vehicles over their lifetime.

Question: What are the current challenges faced by EV charging stations, and how can single board computing technology address these challenges?
Answer. There are several challenges faced by EV charging stations, including:
- Network reliability: EV charging stations require reliable network connectivity to communicate with the electric grid and other charging stations. However, network outages and disruptions can prevent chargers from communicating with each other and with the grid, leading to delays and interruptions in charging.
- Energy management: EV charging stations must be able to manage energy usage to avoid overloading the electric grid and ensure that all vehicles can be charged efficiently. However, this can be a complex task, especially during times of peak demand.
- Payment and billing: EV charging stations must be able to process payments and generate accurate billing statements for customers. However, this can be a challenge, especially when different charging stations and networks use different payment systems and protocols.
Single board computing (SBC) technology can help to address these challenges in several ways, including:
- Network connectivity: SBCs can be used to provide reliable and secure network connectivity for EV charging stations, helping to ensure that chargers can communicate with each other and with the grid even in the event of network outages or disruptions.
- Energy management: SBCs can be used to implement intelligent energy management systems for EV charging stations, allowing them to optimise energy usage and avoid overloading the grid during peak demand periods.
- Payment and billing: SBCs can be used to implement secure and standardised payment systems for EV charging stations, allowing customers to easily pay for charging services and ensuring that accurate billing statements are generated.
Overall, SBC technology can help to improve the reliability, efficiency, and convenience of EV charging stations, helping to accelerate the transition to electric mobility.

Question. Many cars are bought on PCP, which means the GFV (balloon payment) is important. The value of an EV has plummeted lately (look at what Tesla did to their prices), which has resulted in GFVs being very low compared to the upfront cost resulting in very high monthly prices. Is there anything that will affect this positively?
There are several factors that could potentially have a positive impact on the guaranteed future value (GFV) of electric vehicles (EVs), and help to reduce the monthly payments for customers who choose to buy an EV on PCP:
- Improved battery technology: As battery technology continues to improve, the range and performance of EVs is likely to increase, making them more appealing to buyers and helping to maintain their resale value over time.
- Government incentives: Many governments around the world are offering incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of EVs, such as tax credits, rebates, and grants. These incentives can help to make EVs more affordable and attractive to buyers, which could help to maintain their resale value.
- Charging infrastructure: As the network of EV charging stations continues to expand, it will become more convenient and practical for people to own and use EVs, which could help to maintain their resale value.
- Increased consumer awareness: As more people become aware of the benefits of EVs, such as lower operating costs, improved environmental performance, and better performance, demand for these vehicles is likely to increase, which could help to maintain their resale value.
However, it’s important to note that the resale value of any vehicle is influenced by a wide range of factors, including market conditions, supply and demand, and the overall condition and maintenance of the vehicle. While the factors listed above may help to support the resale value of EVs, there is no guarantee that GFVs will rise in the future.
Useful Links
- Webinar Recording on Youtube
- The ROCK SBC Shop on OKdo
- Learn more about ROCK from Richard Curtin, the CTO and co-founder of OKdo
- Learn more about our EV Charging Solutions
- Get in touch with us

Let’s Work Together to Build the Future
Fill in the short form below and one of our expert team will be in touch to guide you to the right products & services for your current or upcoming project.
With a blend of expert technical knowledge and commercial partnerships alongside innovative design & manufacturing capabilities, together we can achieve great things.