What’s included in the blog?
Let us introduce you to LoRa technology, LoRaWAN gateways, Helium-compatible hotspot miners and crypto mining. This blog explains everything you need to know about this high-efficiency long-range network and all the unique applications you can benefit from.
You are probably familiar with WiFi and how widely it has broadened our opportunities. But WiFi, as well as Bluetooth, have a limited coverage range and relatively high energy consumption levels, often referred to as a PAN, Personal Area Network as they cover the nearby vicinity.
Imagine someone tells you that there is a technology available to provide even more wireless coverage and connect even more things efficiently, facilitating the creation of smart homes, cities and industrial centres?
As technology advances, new IoT solutions enter the market, helping industries grow significantly, and private users benefit from extra technological capability. Get yourself a pen and paper, and let’s discover some fantastic technology that brings wireless connectivity to a new level.
What is LoRa?
LoRa technology is a long-range and low-power wireless communications protocol that’s steadily becoming the ‘go-to’ wireless platform of the Internet of Things (IoT). Its story began in 2009 in France when its founders aimed to develop a long-range and low-power modulation technology. The invention was later acquired by an American company called Semtech in 2012.
How does LoRa send data?
Semtech’s LoRa chipsets connect sensors to the Cloud and enable real-time communication of data and analytics that can be used to enhance efficiency and productivity. LoRa devices allow the implementation of smart IoT solutions that solve some of the biggest challenges facing our planet: pollution control, energy management, natural resource reduction, and infrastructure efficiency.
Multiple LoRa gateways receive data transmitted by a LoRa node; then, the gateways forward the received data to a centralized network server (IoT server).
How far can LoRa transmit?
LoRa is short for ‘long range’, as this technology provides long-range communications coverage, allowing you to connect devices up to 3 miles (five kilometres) in urban areas and up to 10 miles (15 kilometres) or more in rural areas.
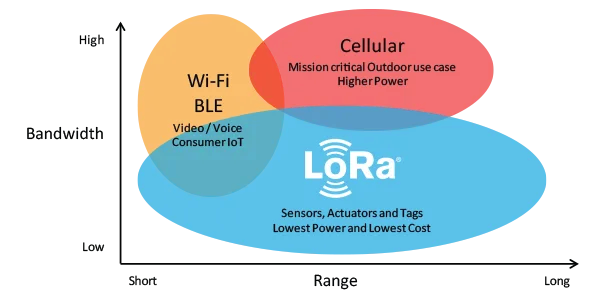
Key features of LoRa:
- Long-range
- Low Power
- Secure connection
- Standardized
- Geolocation tracking
- Mobile
- High capacity
- Low cost
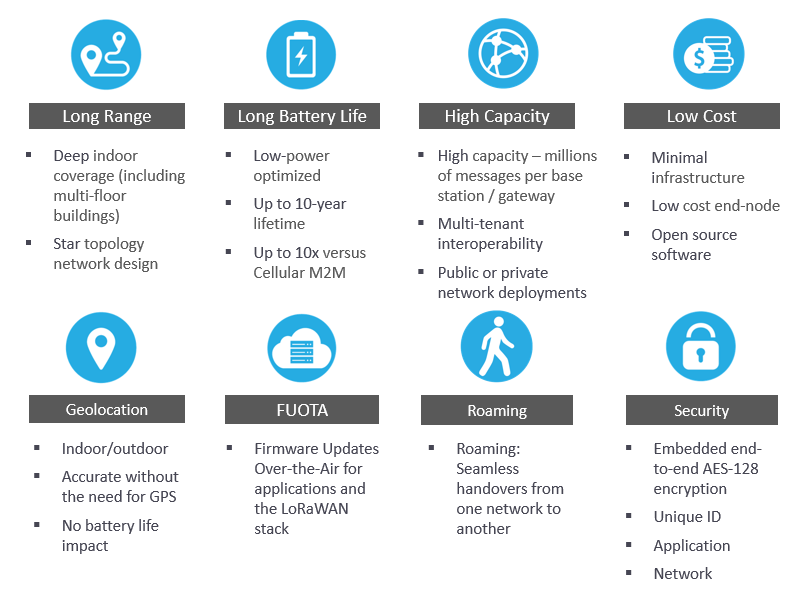
One of the key features of the solutions built with LoRa chipsets is their ultra-low power requirements. Sensors and other devices made with LoRa chips can last for up to 10 years on a single battery.
LoRa devices offer incredible features for IoT applications, including long-range, low power consumption and secure data transmission. This innovative technology is widely used by public, private or hybrid networks and provides a wider range than Cellular networks.
What is the use of LoRa?
What can you do with LoRa? Almost everything! With an ever-increasing number of IoT applications, LoRa devices and the LoRaWAN protocol create efficient business solutions and improve lives worldwide.
These are some key applications of the LoRa technology:
- Smart agriculture
- Smart buildings
- Smart cities
- Smart metering (electricity, gas, water)
- Smart environment
- Smart healthcare
- Smart homes
- Smart industrial control
- Smart retail
- Smart supply chain and logistics
LoRa allows you to create IoT solutions for various use cases worldwide. For example, in Africa, LoRa is used for combating the poaching of wildlife. In Calgary and Glasgow, the technology helps manage entire cities – from monitoring air quality to public transportation.
On a smaller scale, LoRa and LoRaWAN are being used to maximize the efficient use of office space. Some other use cases answer simple questions such as “Does the bus have room for more people?” and “How long is the line in the cafeteria?” making business and life easier to manage.
Also, LoRa technology is ideal for implementing smart water metering systems, or even smart parking systems, helping manage traffic congestion created by drivers looking for a place to park.
What is the difference between WiFi and LoRa?
WiFi is limited in range and has high energy consumption. It covers short- and medium-range connections at high data rates, making it the most suitable technology for user-centric applications like real-time video and Internet browsing.
In contrast, LoRa covers long-range use cases at low data rates, making it the ideal technology for low bandwidth applications, including locations that are hard to reach, such as temperature sensors in a manufacturing setting.


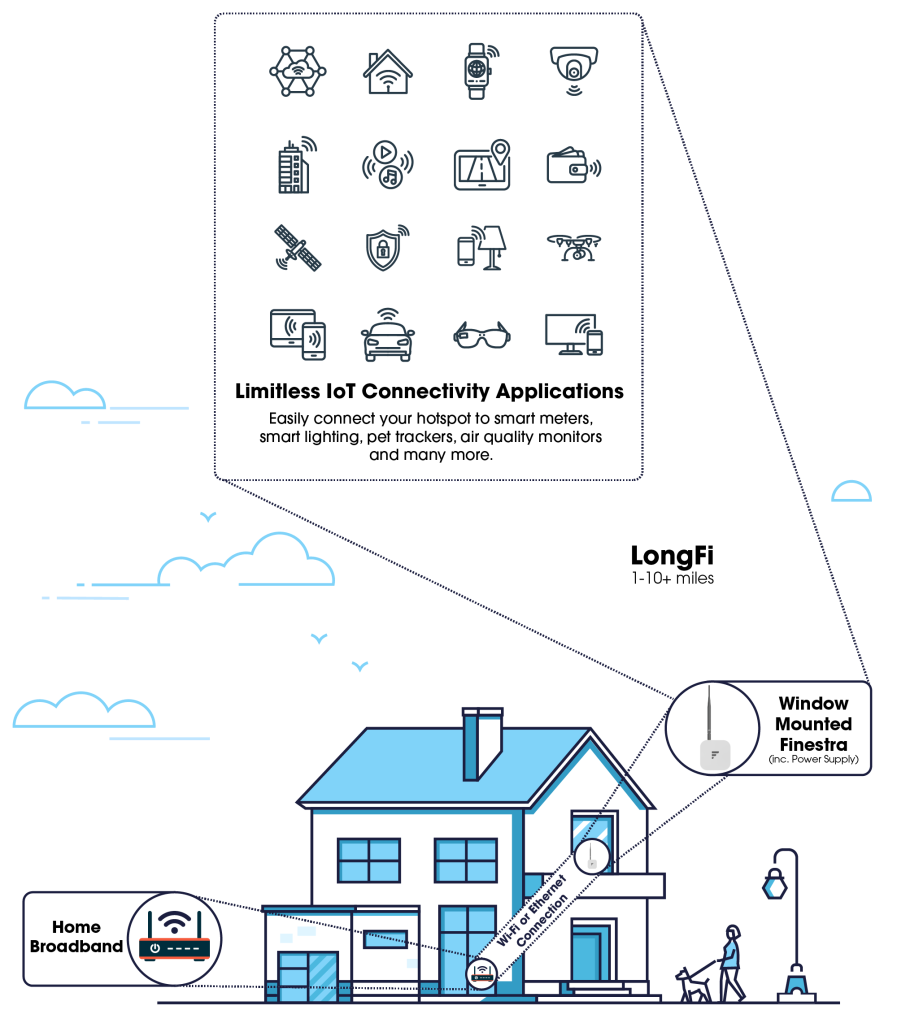
LoRa is specially designed for IoT devices and gives long-range transmissions of 1-10+ miles away using LongFi Technology, enabling thousands of IoT devices to connect to a single LoRaWAN hotspot. It transfers over much longer ranges than WiFi (typically more than 200x WiFi).
Is LoRa free?
Yes, LoRa is free! According to Semtech, LoRa enables devices to translate data into RF (radio frequency) signals, sending messages over the air using chirp spread spectrum communications and the license-free sub-gigahertz frequency bands.
What is LoRaWAN technology?
LoRaWAN is an open, cloud-based networking protocol that delivers secure bi-directional communication, mobility, and localization services standardized and maintained by the LoRa Alliance.
In simple words, LoRaWAN uses LoRa wireless technology and adds a networking component to it. Additionally, it incorporates node authentication and data encryption, making the network secure.
What’s more, LoRaWAN networks are perfect for IoT devices that continuously monitor a process/installation status, as they can trigger alerts back to gateways when the monitored data exceeds a set threshold. These IoT devices require little bandwidth and can run on battery power for months or even years.
What is the difference between LoRa and LoRaWAN?
From a networking perspective, whilst LoRa creates only a physical layer method of wireless transport, such as a transceiver chip, LoRaWAN is a networking protocol that enables devices to communicate wirelessly with LoRa.
Since LoRa lacks the proper network capabilities required to manage data collection and endpoint device management traffic, LoRaWAN, or long-range WAN, comes into play. LoRaWAN is a protocol that builds on top of LoRa and creates the network layer.
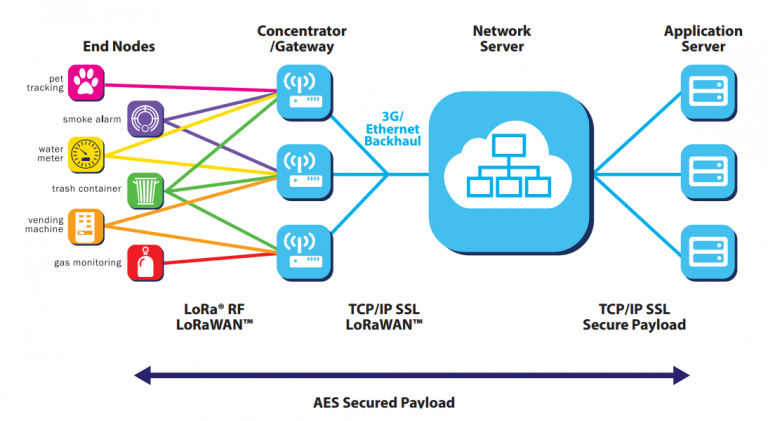
The LoRaWAN Network Architecture
To understand the network better, let’s have a look at the LoRaWAN network architecture presented by The Things Network:
- End Nodes – Represent edge devices or sensors.
- LoRaWAN Gateway – Collects or concentrates data from several end nodes.
- Network Server – Consolidates data from gateways for uploading it to the application server.
- Application Server – Processes or displays consolidated data.
What is a LoRaWAN gateway?
As we’ve already covered what LoRaWAN technology is, let’s clarify what is a LoRaWAN gateway. In simple words, a gateway is a physical plastic box that incorporates the hardware and application software that allows connecting IoT devices to the cloud. To understand this better, we can compare a gateway with a WiFi router.
Let’s view the gateway as an intermediary that allows LoRaWAN end devices to transmit data to the cloud. Usually, a gateway can be for indoor or outdoor use, and they have various antenna options, allowing them to cover different ranges.
What is a LoRaWAN gateway used for?
The LoRaWAN gateway communicates with IoT devices through the LoRaWAN network; they are connected to the network through WiFi, Ethernet or cellular to provide end-to-end connectivity between LoRa end nodes and the application server.
A more scientific explanation is that a LoRaWAN gateway receives LoRa modulated RF messages from any end device in hearing distance and forwards these data messages to the LoRaWAN network server (LNS), which is connected through an IP backbone.
What products are compatible with the LoRaWAN technology?
To make the most out of the opportunities given by the LoRaWAN technology, the industry has developed various products compatible with LoRaWAN. These are software and hardware products allowing wireless communication using the LoRaWAN technology. Some available LoRaWAN compatible hardware includes antennas, development boards, sensors, gateways, modules and microcontrollers.
In summary, the key points of LoRaWan are:
- LoRaWAN provides long-distance coverage, making it ideal for urban and rural solutions.
- It requires less power which makes the technology ideal for battery-powered devices.
- LoRaWAN provides low bandwidth communication, making it ideal for practical IoT applications requiring less data.
- Relatively low deployment costs compared to mobile or WiFi due to the fewer gateway devices required.
- LoRaWAN supports bi-directional communication.
- A single LoRaWAN gateway can accommodate 1,000s of devices or nodes, whilst multiple gateways can provide connectivity to numerous smart solutions.
What is a Helium network?
The Helium network is a decentralized wireless network that allows devices worldwide to wirelessly connect to the Internet and geolocate themselves with no need for high power-consuming satellite location hardware or expensive cellular plans.
Helium is a blockchain-based network for IoT devices that uses nodes as Hotspots to connect wireless devices to the network. It is also called “the People’s Network”. You can view the network map here.
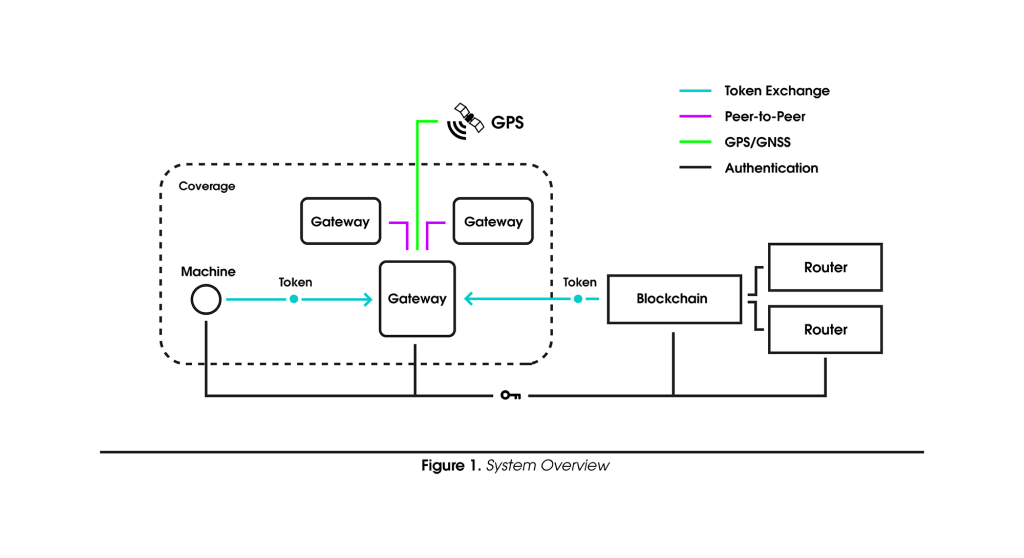
There are 3 types of participants in the Helium network: the IoT device, the Miner and the hotspot (or gateway). Miners, users who own a Helium compatible gateway and provide wireless connectivity to the Helium Network, have the opportunity to mine cryptocurrency, meaning they can earn HNT tokens for providing network coverage.
What is a Helium miner hotspot, and what does a Helium miner do?
A Helium miner hotspot allows you to own, set up and operate a wireless network for IoT devices. Helium compatible hotspots are devices that take the form of hardware containing a radio chip and firmware; they spend tokens by paying Miners to send data to and from the Internet.
Miners can earn HNT tokens (Helium coins) by providing wireless network coverage via hardware (gateways/hotspots).
What is Helium HNT?
HNT (Helium coins/tokens) is a cryptocurrency that can be earned when Helium compatible hotspots provide and validate wireless coverage and send device data over the network.
Helium hotspots earn HNT coins for building secure network infrastructure and transferring data. The amount of HNT coins earned by each hotspot depends on the value provided to the network. The Helium blockchain uses an algorithm called Proof-of-Coverage (PoC) to validate each hotspot’s contribution to the network. PoC aims to verify that hotspots are located where they claim to be.

Therefore, to ensure the PoC algorithm considers the value your hotspot provides to the People’s Network, multiple hotspots must be located in your area at least 300 meters apart but still within a few miles range from each other. That’s why single hotspots may earn less as they can’t participate in Proof-of-Coverage.
You can find a more detailed explanation of how exactly HNT coins are earned on the Helium website.
What is crypto mining?
Cryptocurrency mining, or crypto mining, is the process where specialized computers, also known as nodes or mining rigs, validate blockchain transactions for a specific crypto coin and, in turn, receive a mining reward for their effort of ensuring connectivity to the network.
In simple words, crypto mining is how units of cryptocurrency are created. How does this work? Crypto is mined by resolving complicated mathematical equations faster than your competition.
But what is cryptocurrency? Crypto is a digital asset, a digital currency, bought and sold online. It is designed to serve as a medium of money exchange online without relying on a central authority, such as a bank or a government.
Discover our range of LoRa and Sigfox products below!

LoRA & Sigfox
Are you still looking for more inspiration? Let’s have a look at our Projects Hub, Getting Started Guides and Blogs!






